Atlas of the average human heart created from 3D CT images
6 March 2013
Researchers at Pompeu Fabra University in Spain have created a high resolution atlas of the human heart by using statistical analysis to average the complex data of 3D images taken from 138 people.
The study demonstrates that an average image of an organ along with its variations can be obtained to compare individual cases and differentiating healthy forms from pathologies.
Scientists have created a representation of the average shape of the heart and its variations with images in 3D from 138 fully functioning hearts taken using multislice computed tomography (CT).
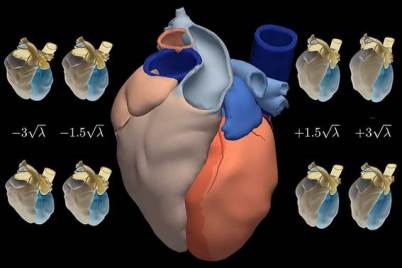
Atlas of the human heart generated by
statistical analysis of 3D CT images. Source: Pompeu Fabra
University
"This atlas is a statistical description of how the heart and its components, such as the ventricles and the atrium, look," said Corné Hoogendoorn, researcher at the CISTIB centre of the Pompeu Fabra University. "In our analysis the population group included 138 people but it could be applied to much larger populations. We demonstrated the feasibility of constructing this type of atlas using many subjects, with an acceptable level of manual parameter tuning, while still providing good numeric results".
To create this cardiac map the researchers developed a statistical model capable of managing high quantities of information provided by individual images. It can also collect temporary variations, given that the heart is never motionless.
The level of detail and the possibility to extend the atlas give it an advantage over the majority of cardiac models present to date. The researchers believe that the study can be applied to medical image processing, especially when segmenting, or in other words, properly differentiating a structure to be analysed from the rest of the image.
"The statistics of the atlas offer a continuous range of exemplary heart shapes, which allows for the comparison of concrete cases as well as the calculation of probabilities of the latter belonging to the modelled population," said Hoogendoorn.
The method can be applied to the images of any other organ or structure. It has the advantage of providing the ability to classify and diagnose healthy shapes and pathologies as well as to differentiate between different illnesses and even establish grading amongst each.
In addition, computational simulations of the heart electrophysiology and mechanics (as well as the mechanics of other organs) can be based on the atlas, which can help to better plan treatment for patients.
Reference
Hoogendoorn C. A High-Resolution Atlas and Statistical Model of the Human Heart From Multislice CT. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 32 (1): 28-44, 2013. Doi: 10.1109/TMI.2012.2230015.